How Should You Train Your Roomate To Clean With Disequilibrium Principle
Original Editor - Bart Moreels
Elevation Contributors - Bart Moreels, Sheik Abdul Khadir, Kim Jackson, Daphne Jackson, Tony Lowe, Scott Buxton, Evan Thomas, Naomi O'Reilly, Sinead Greenan, WikiSysop, Karen Wilson, Claire Knott, Lauren Lopez and Admin
Introduction [edit | edit source]
The Romberg test is an advisable tool to diagnose sensory ataxia, a gait disturbance acquired by abnormal proprioception involving information about the location of the joints. It is too proven to exist sensitive and accurate means of measuring the caste of disequilibrium acquired by central vertigo, peripheral vertigo and head trauma.[1] It has been used in clinic for 150 years [2]
Purpose [edit | edit source]
The Romberg exam is used to demonstrate the furnishings of posterior cavalcade disease upon human being upright postural control. Posterior column disease involves selective dissentious of the posterior column, known as tabes dorsalis neurosyphilis. The Romberg exam is used for the clinical cess of patients with disequilibrium or clutter from sensory and motor disorders.
Equilibrium is defined as any status in which all interim forces are cancelled by each other resulting in a stable balanced system. Information technology is maintained through the sensory information from vestibular, somatosensory and visual systems. A patient who has a problem with Proprioception (Somatosensory) can still maintain balance past compensating with vestibular function and vision. In the Romberg test, the patient stands upright and asked to close his optics. A loss of residual is interpreted equally a positive Romberg sign.
The Romberg examination was first described in 1846 and was originally described for the status tabes dorsalis. Before performing the Romberg exam, information technology is necessary to test other aspects of the patient's balance when potential issues with clutter or disequilibrium are present. Often, proprioceptive challenges are not the first problems faced by this population. Sometimes, it is more simple. It is important to first assess other aspects of residual harm in order to rule out confounding factors that could lead to a faux positive examination[iii] [4].
Clinically Relevant Anatomy [edit | edit source]
There are 3 sensory systems that provide input to the cerebellum to maintain truncal stability when the eyes are open:
- Vision
- Proprioception
- Vestibular sense
Only two of the three systems are needed to maintain balance. When visual input is removed, instability due to lack of vision can be teased apart from other sensory impairments. If in that location is a more astringent proprioceptive or vestibular lesion, or if there is a midline cerebellar lesion causing truncal instability, the patient will exist unable to maintain the continuing position, fifty-fifty when the eyes are open. Note that instability can too be seen with lesions in other parts of the nervous organization, such as the upper or lower motor neurons, or the basal ganglia[5] [6].
Technique [edit | edit source]
The Original Romberg test [edit | edit source]
The exam is performed as follows:
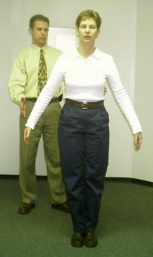
- The patient is asked to remove his shoes and stand with his two feet together. The artillery are held next to the body or crossed in front end of the body.
- The clinician asks the patient to first stand quietly with eyes open, and subsequently with eyes closed. The patient tries to maintain his residual. For safety, it is essential that the observer stand close to the patient to prevent potential injury if the patient were to fall. When the patients closes his optics, he should not orient himself by light, sense or sound, as this could influence the exam upshot and crusade a simulated positive consequence.
- The Romberg test is scored by counting the seconds the patient is able to stand up with eyes closed.
- The literature does not report alternative methods for scoring a Romberg test.
- To make the Romberg examination more difficult, the clinician tin attempt to disturb the patient's remainder with a perturbation. It is important that the clinician does non exaggerate the perturbation.
- A Romberg exam can also be used as follow-up assessment for patients with residuum and/or proprioception impairments by comparing several different assessments with each other.
- If the clinician observes that the patient is able to stand for longer periods of time with the eyes airtight, it is axiomatic that the patient's residual and proprioceptive deficits have decreased[3] [7] [4] [eight].
- The Romberg test is positive when the patient is unable to maintain residual with their eyes closed. Losing balance can exist defined as increased torso sway, placing one foot in the direction of the fall, or even falling.
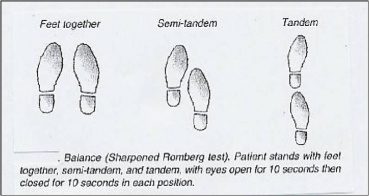
The Sharpened or Tandem Romberg exam [edit | edit source]
The Sharpened or Tandem Romberg examination is a variation of the original test. The implementation is mostly the aforementioned. For this second test, the patient has to identify his feet in heel-to-toe position, with one foot direct in front of the other. As with the original Romberg test, the assessment is performed first with eyes open and so with eyes airtight. The patient crosses his arms over his breast, and the open palm of the mitt lies on the reverse shoulder. The patient likewise distributes his weight over both his feet and holds his chin parallel with the flooring[seven] [4].
Obese and older individuals may be unable to stand up in this position for prolonged periods of fourth dimension. For these populations, the Romberg test does not exclusively demonstrate proprioceptive impairments in comparison to other misreckoning factors[3].
Variables [edit | edit source]
Although a patient with an acute peripheral vestibular lesion is ordinarily inclined to move towards the side of the problem, it has been shown that chronic vestibular impairment (at least fractional compensation) does not produce deficits in the standard Romberg test. Likewise, an individual with proprioceptive problems, accompaniment to tabes dorsalis, would exist unable to stand up with the eyes closed and feet together[3].
Many believe that the sharpened Romberg test is a amend indicator of vestibular damage than the original Romberg exam. The sharpened Romberg examination results give an objective measure out of postural stability. This can aid to quantify ataxia[3].
Subject, sex, and age do not create a statistically pregnant difference between normal subjects between the ages of 20 and 49 years; only the Romberg sharpened test with eyes open provided a significant difference (p< 0.05) between men and women. Greater instability in subjects less than twenty and more fifty years of age was likewise exhibited. When comparing a immature and an old accomplice, at that place is a significant difference in performance.
Increasing the difficulty of the tandem Romberg test for patients is not helpful because it too makes the tests more difficult to perform for controls with no symptoms of vestibular disease. This would also go far harder to evaluate the test results. Decreased performance times on the modified Romberg is associated with a concomitant rise in the risk of falling[4] [9] [10].
Reliability and Validity [edit | edit source]
There is no consensus in the Reliability (Intra and inter) and validity for Romberg'due south in the literature as the test is more of qualitative rather than quantitative (Objective). However, this test can be used as a quick clinical tool to screen. The introduction of various instrument in the loonshit of balance assessment and the strength platform usage has given the more objective and accurate measurement.
Limitations[11][12] [edit | edit source]
- Non Quantitative
- Low diagnostic sensitivity and specificity
- Low power to determine lesions, predict the risk of falling and reverberate the discomfort and ability to perform daily activities.
References [edit | edit source]
- ↑ Soochan Kim, Mijoo Kim, Nambom Kim, Sungmin Kim, Gyucheol Han.Quantification and Validity of Modified Romberg Tests Using Three-Centrality Accelerometers.Green and Smart Technology with Sensor Applications. Communications in Computer and Informatics Volume 338, 2022, pp 254-261.
- ↑ Reicke, North.: The Romberg head-shake examination within the telescopic of equilibrium diagnosis. H.N.O forty, 195–201 (1992)
- ↑ 3.0 three.1 3.two 3.3 three.4 Goebel JA. Practical direction of the dizzy patient. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2008.
- ↑ 4.0 4.i 4.2 iv.three Black FO, et al. Normal subject area postural sway during the Romberg examination. Am J Otolaryngol. 1982 Sep-Oct;3(5):309-18.
- ↑ Blumenfeld, H. Neuroexam.com - Romberg test. www.neuroexam.com/neuroexam/content.php?p=37 (accessed 31 Dec 2022).
- ↑ Zelczak TA. Neurologic examination. www.pacificu.edu/optometry/ce/courses/15840/neuroexampg3.cfm (accessed 31 December 2022).
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Johnson BG, et al. The sharpened Romberg examination for assessing ataxia in balmy acute mountain sickness. Wilderness Environ Med. 2005 Summertime;xvi(2):62-half-dozen.
- ↑ Brinkman DMC, et al. Kwantificering en evaluatie van v neurologische evenwichtstests bij proefpersonen en patiënten. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1996;140:2176-fourscore.
- ↑ Longridge NS. Clinical Romberg testing does not find vestibular disease. Otol Neurotol. 2022 Jul;31(v):803-half dozen.
- ↑ Agrawal Y. The modified Romberg rest test: normative data in Usa adults. Otol Neurotol, 2022 Oct,32(8):1309–1311.
- ↑ McMichael,Grand.A., Vander, B.J., Lavery, L., Rodriguez, E., Ganguli, Thou.: Simple balance and mobility tests can assess falls risk when cognition is dumb. Geriatr. Nurs. 29, 311–323 (2008)
- ↑ O'Neil, D.E., Gill-Body, One thousand.M., Krebs, D.E.: Posturography changes do not predict functional performance changes. Am J. Otol. xix, 797–803 (1998)
Source: https://www.physio-pedia.com/Romberg_Test
Posted by: maydins1939.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Should You Train Your Roomate To Clean With Disequilibrium Principle"
Post a Comment